You customise a battery charger and BMS integration for industrial systems by defining the battery chemistry, voltage range, power level, and communication logic at the system design stage, not after hardware selection.
This system-level approach ensures the charger operates as a controlled energy component rather than a generic power supply. In industrial applications, batteries, loads, and control electronics interact continuously, which makes early-stage customisation essential for safety, efficiency, and long-term reliability.
Why Is System-Level Customisation Critical in Industrial Charging?
Unlike consumer chargers, industrial battery chargers must operate under variable loads, harsh environments, and long duty cycles. Therefore, engineers cannot treat the charger and the Battery Management System (BMS) as isolated components.
Instead, the charger, battery pack, and BMS form a closed-loop system. When this loop is designed correctly, the system achieves stable charging behaviour, predictable thermal performance, and accurate state-of-charge estimation. Otherwise, mismatched parameters often lead to overheating, shortened battery life, or unexpected system shutdowns.
How Battery Chemistry Defines Charger and BMS Design
The first step in custom battery charger design is identifying the battery chemistry. Lead-acid, lithium-ion, and LiFePO4 batteries each require distinct charging algorithms and protection logic.
For example, a custom SLA battery charger must manage bulk, absorption, and float stages precisely. In contrast, a custom LiFePO4 battery charger prioritises voltage accuracy and strict over-voltage protection. When paired with a compatible BMS, the charger can dynamically adjust current and voltage based on real-time cell feedback.
This chemistry-driven approach is widely applied in custom battery charger projects designed for industrial power equipment and energy storage systems.
Voltage and Power Range: From Low Power to High Output Systems
Industrial systems often operate across wide voltage and power ranges. Custom chargers may cover anything from low-voltage control batteries to high-power energy storage modules.
For instance, Phonix Technology develops chargers supporting wide operating windows such as 6V–84V and scalable power levels from tens of watts up to several kilowatts. This flexibility allows one platform to serve multiple applications while maintaining stable performance.
More importantly, power capability must align with battery capacity. A custom 18650 battery charger designed for compact packs differs significantly from a custom 21700 battery charger used in higher-capacity industrial modules. Matching current limits to cell specifications protects both the battery and the charger.
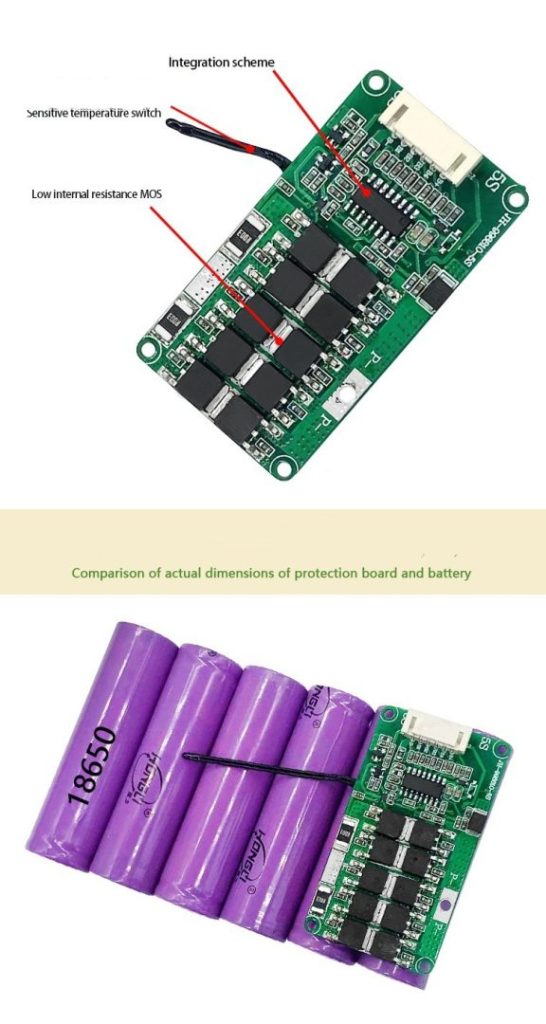
How BMS Communication Improves Charging Accuracy
BMS integration transforms a charger from a fixed-output device into an adaptive energy controller. Through digital communication, the BMS provides real-time data such as cell voltage, temperature, and protection status.
As a result, the charger can adjust charging parameters dynamically. If the BMS detects abnormal temperature rise or cell imbalance, the charger responds immediately by reducing current or pausing the charging process.
This level of interaction is common in BMS-integrated charging solutions used in industrial automation, robotics, and AI-powered systems.
Custom Charging Profiles for Different Battery Capacities
Battery capacity also influences charger behaviour. Industrial systems may use packs ranging from a few amp-hours to tens or hundreds of amp-hours.
For example, chargers designed for 3Ah, 5Ah, or 10Ah battery packs require different current scaling compared to systems using 20Ah or larger modules. By defining capacity-specific profiles, engineers ensure optimal charging speed without exceeding thermal or electrical limits.
This approach applies equally to lithium-based systems and lead-acid configurations, including custom wet battery chargers and custom dry battery chargers used in backup power and industrial mobility.
Safety and Protection as Part of the Custom Design
Safety mechanisms must be embedded at both charger and BMS levels. Over-voltage, over-current, short-circuit, and thermal protection cannot rely on a single layer.
Instead, a well-designed system distributes protection logic across hardware, firmware, and communication protocols. This layered strategy ensures fault tolerance even if one component reaches its limit.
Where Custom Charger and BMS Integration Is Commonly Used
Customised charging systems are widely deployed in energy storage cabinets, industrial power tools, smart mobility platforms, and AIoT devices. In these applications, stable energy management directly affects system uptime and operational cost.
By integrating the charger and BMS from the start, manufacturers gain better control over performance, compliance, and long-term maintainability.
Why Phonix Technology Focuses on Custom Integration
Phonix Technology designs smart battery chargers and BMS solutions as unified systems rather than separate products. This philosophy allows engineers to tailor voltage, current, communication protocols, and protection logic according to real industrial requirements.
As a result, customers receive solutions that fit their applications precisely instead of adapting their systems to off-the-shelf chargers.