Portable electronic devices are now deeply integrated across consumer, medical, industrial, and automotive sectors. As their performance and energy demands increase, the charger is evolving from a simple power accessory into a critical energy management component that directly influences device lifespan, stability, and user experience.
1. High-Power Charging Is Becoming the Standard
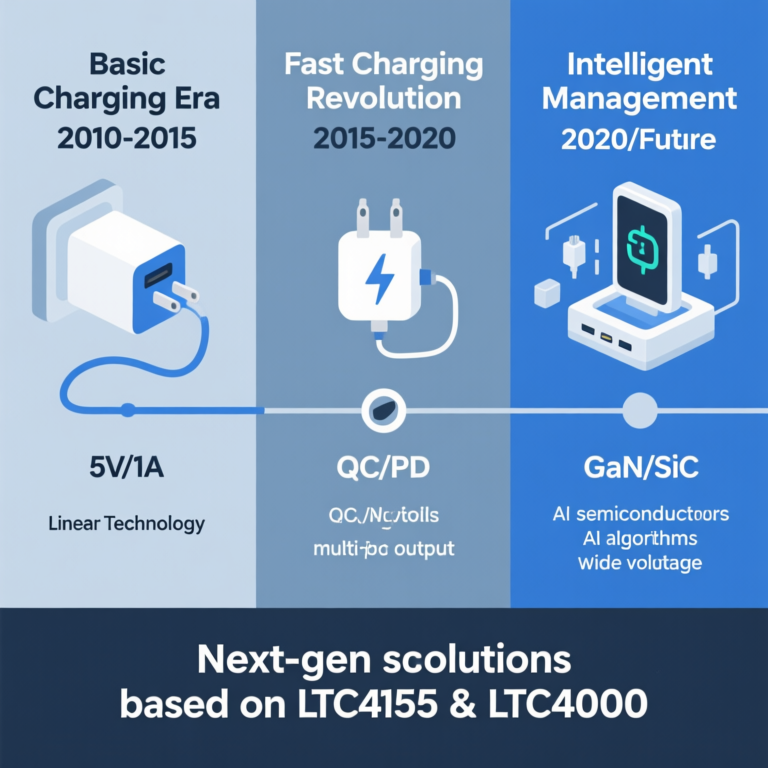
Modern handheld devices combine multi-mode connectivity, high-resolution displays, and continuous sensing workloads—leading to rising power consumption. While increasing battery voltage can reduce current stress, the 5V fast-charging architecture remains mainstream due to cost and design considerations.
For devices with multi-thousand-mAh lithium battery packs, charging must be fast, controlled, and thermally safe. This is where intelligent high-power chargers demonstrate their value, balancing speed with battery longevity.
Take the LTC4155 power management IC as an example—it showcases what modern fast-chcharging technology can achieve:
- Supports >3A charging with 88%–94% efficiency
- Multi-source power path control for flexible input switching
- Configurable via I²C for adaptive charging behavior
This marks the shift from “charging quickly” to “charging efficiently and intelligently.” Such chips are commonly utilized in high-performance portable device chargers, especially those designed for tablets and industrial handheld terminals.
2. Wide Input Voltage Capability Enables True “Charge Anywhere” Usage
Users increasingly expect their devices to charge not only from wall adapters, but also from diverse power sources such as:
- Solar panels with variable output
- 12V/24V vehicle power systems
- Industrial or telecom-grade power rails
Traditional chargers limited to <30V input often fail under these conditions, creating clear demand for wide voltage smart charging solutions.
Components like the LTC4000 controller have made this possible by offering:
- 3V–60V input compatibility
- Support for buck, boost, and buck-boost topologies
- Compatibility with multiple battery chemistries
Such flexibility allows a single charger architecture to scale from consumer electronics to industrial charging equipment, a trend well documented in resources like EE Times on power design evolution.
3. Intelligent Charging Management Defines Next-Generation Chargers
It’s no longer just about transferring energy—modern intelligent charging systems integrate multiple advanced features:
- Adaptive power path management that prioritizes system load
- Thermal-aware charging control using NTC monitoring
- Chemistry-specific charging curves for Li-ion, SLA, or NiMH batteries
- System-level protection against overvoltage and reverse current
The goal has shifted from merely injecting charge to maximizing battery health while ensuring stable device performance under all conditions. Brands like Phonix Charger have incorporated similar logic into their latest smart charging adapter series, emphasizing both reliability and programmability.
4. Technology Convergence Shapes the Next Wave
Looking ahead, several technological forces will redefine what chargers can do:
| Trend | Impact |
|---|---|
| Higher power density via GaN/SiC | Smaller and cooler chargers |
| Predictive, adaptive charging algorithms | Longer battery lifespan |
| Full-environment power compatibility | Broader application scenarios |
Wider adoption of gallium nitride (GaN) chargers, for instance, allows higher switching frequencies and reduced heat loss—addressing key bottlenecks in high-power portable charging. More design references can be found in technical publications such as Power Electronics News.
Conclusion
As portable devices grow more capable and energy-intense, the charger will continue to evolve from a peripheral into a strategic component in the overall power architecture. Manufacturers that master the trio of high-power delivery, wide-voltage adaptation, and intelligent energy management—much like what platforms based on LTC4000 and LTC4155 have demonstrated—will lead the next wave of portable device innovation.

